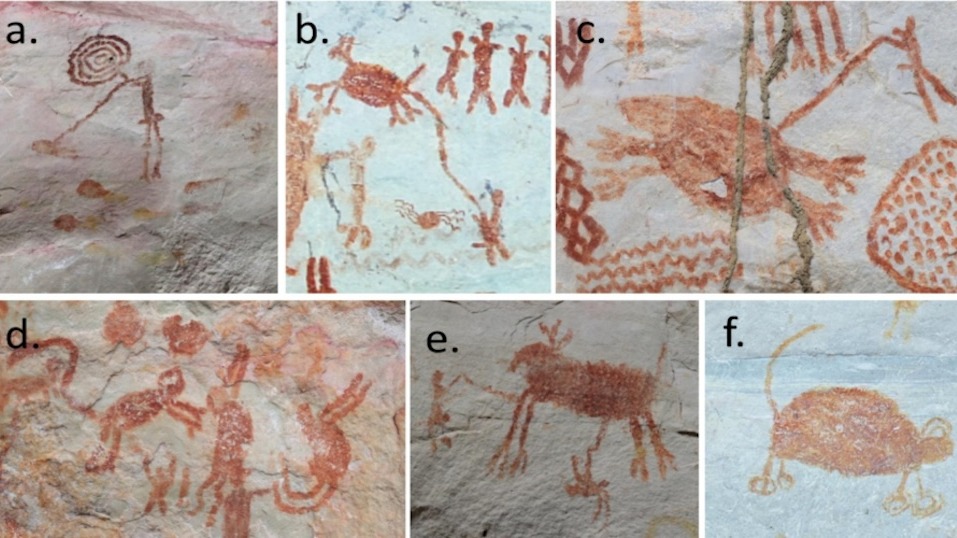
Una galería de fotografías impactantes ocre Las pinturas dibujadas en enormes paredes rocosas ofrecen información sobre la estrecha relación entre los humanos y los animales que vivieron en el Amazonas hace miles de años.
La obra está ubicada sobre afloramientos rocosos del Cerro Azul, en la Serranía de la Lindosa, un acantilado en Colombia. Incluye 3.223 dibujos de humanos y animales, incluida una colección de peces, reptiles y mamíferos de distintos tamaños, según un nuevo estudio publicado en la edición de septiembre de la revista. Revista de Arqueología Antropológica.
Algunas imágenes incluso muestran animales y humanos transformándose entre sí, lo que indica «la rica mitología que ha guiado a generaciones de indígenas amazónicos», según un comunicado de la Universidad de Exeter.
Aunque los investigadores no han fechado formalmente el lienzo, estimaron que existía desde el año 10.500 a.C.
«Estos sitios de arte rupestre incluyen la evidencia más antigua de presencia humana en la Amazonía occidental, que data de hace 12.500 años», dijo el autor principal. Marcos Robinsondijo en el comunicado profesor asociado del Departamento de Arqueología e Historia de la Universidad de Exeter.
Relacionado: Descubren pinturas rupestres de 9.000 años entre huellas de dinosaurios en Brasil
El equipo descubrió al menos 22 especies de animales, entre ellos venados, aves, pecaríes, lagartos, tortugas y tapires. Después de comparar los dibujos de animales con antiguos huesos de animales cortados descubiertos en excavaciones cercanas, los arqueólogos descubrieron que la representación proporcional de los dibujos por especies no correspondía a la proporción de huesos de animales, lo que indica que los indígenas no solo pintaban lo que ellos comieron. Los huesos cortados incluían una dieta diversa, que incluía peces, mamíferos y reptiles, como serpientes y cocodrilos.
«El arte ofrece una visión asombrosa de cómo estos primeros colonos veían su lugar en el mundo y cómo formaban relaciones con los animales», dijo Robinson. “El contexto demuestra la complejidad de las relaciones de los amazónicos con los animales, como fuente de alimento pero también como seres venerados, que tenían conexiones sobrenaturales y requerían negociaciones complejas por parte de los especialistas en rituales. »
Dada la extensión del arte rupestre, los investigadores optaron por centrarse en seis paneles, incluido El Más Largo, de 40 metros de largo, que contiene 1.000 dibujos, y el panel mucho más pequeño, de 10 metros de largo, conocido como Principal, que contiene 244 imágenes, según el comunicado.
Tras catalogar las obras, los investigadores descubrieron que el 58% de los dibujos eran figurativos, la mitad de los cuales eran imágenes de animales. También observaron escenas que mostraban a personas pescando.
Los investigadores sólo pueden especular sobre el propósito y el significado del arte rupestre.
«Si bien no podemos estar seguros del significado de estas imágenes, ciertamente ofrecen mayores matices a nuestra comprensión del poder de los mitos en las comunidades indígenas», dijo el coautor del estudio. José Iriarte«Estos hallazgos son particularmente reveladores con respecto a los aspectos más cosmológicos de la vida en el Amazonas, como lo que se considera tabú, dónde reside el poder y cómo se llevaron a cabo las negociaciones con lo sobrenatural», dijo el profesor de Arqueología de la Universidad de Exeter. .